1 引言
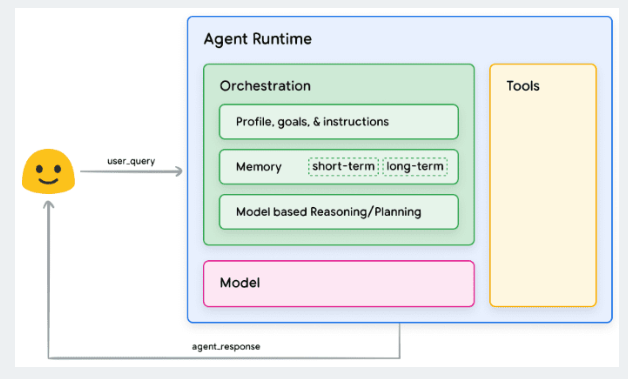
之前谈过agent的组成,base model、编排层和tools。为了更好的构建agent,如何调用tool,将是必不可少的知识点。
最近翻阅各大模型的tools use的文档的时候,发现这块的文档的例子都比较简单。这次通过调用本地的drissionpage来实现一个deepseek一样的联网搜索。
2 效果展示
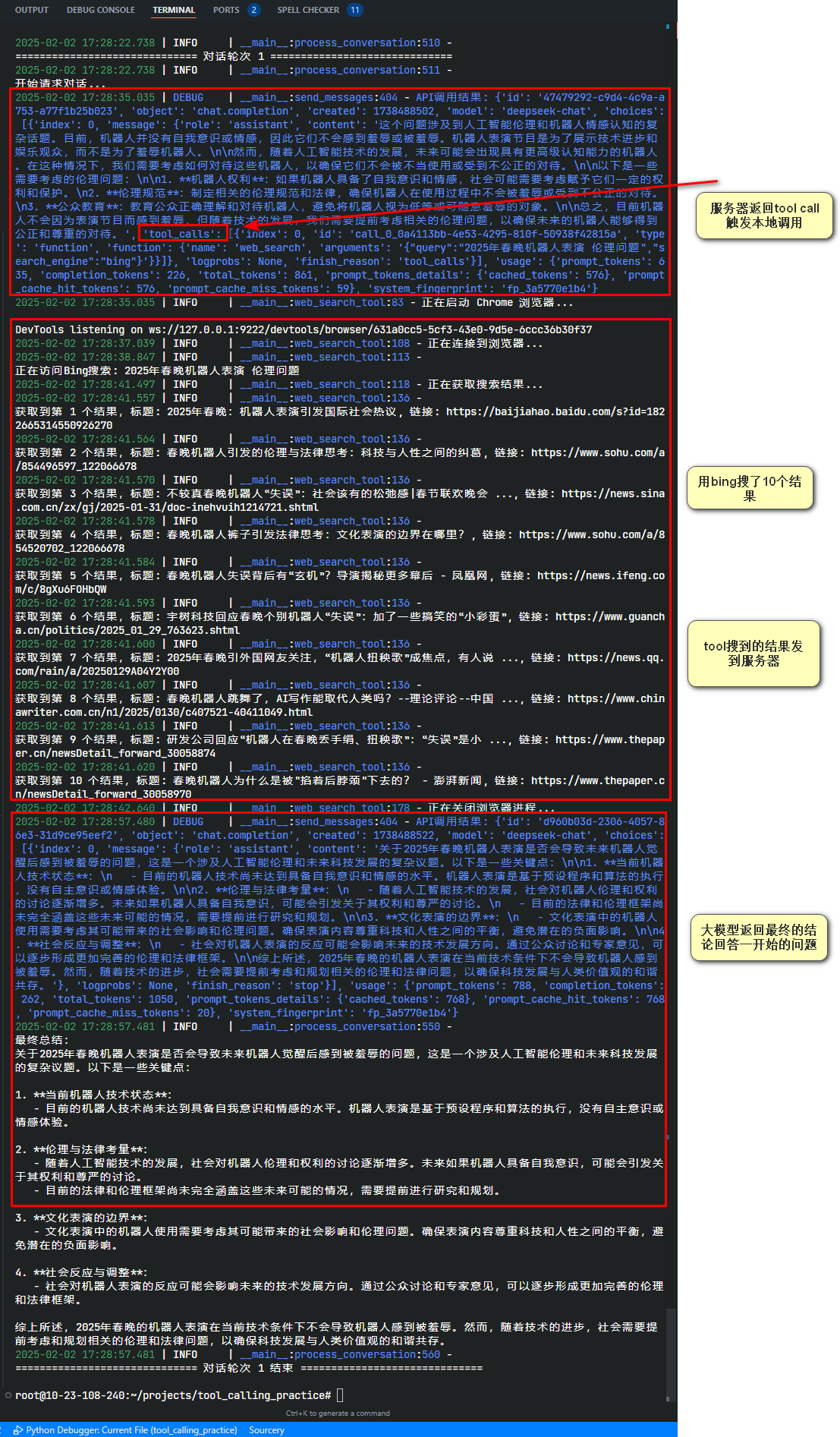
我们用一个最近的例子,让大模型获得访问外部信息的能力。以2025年春晚机器人表演,会导致以后机器人觉醒后认为自己被羞辱么?为问题。
这是第一次,system输入后,大模型知道了自己的执行逻辑。 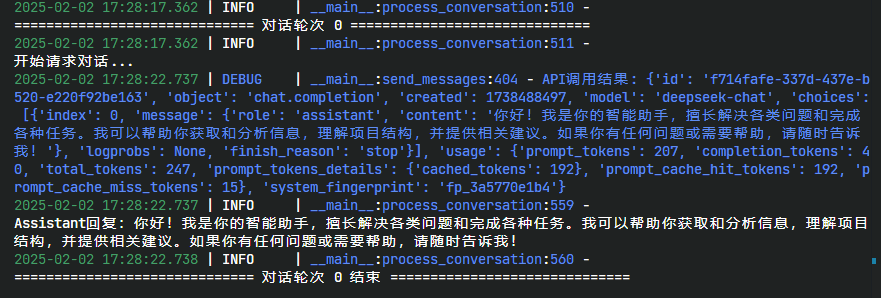 image.png
image.png
于是当user prompt输入后,它开始发现需要调用工具,于是调用了我本地的方法进行搜索,然后进行了总结。
3 tool use 概念及基础
3.1 概念
Tool use(工具使用)是一种让大语言模型能够通过调用外部工具/函数来增强其能力的技术。它建立了一个通用协议,规定了大语言模型如何与其他软件系统进行交互。
尽管不同平台使用不同的术语(OpenAI称为function calling,Anthropic称为tool use,DeepSeek和Qwen也各有叫法),但本质上都是指:让语言模型能够调用外部工具/函数来扩展其能力的机制。为行文清晰,本文统一使用"tool use"来指代这一概念,特定平台相关内容除外。
3.2 tool use 的分类
You can extend the capabilities of OpenAI models by giving them access to
tools, which can have one of two forms:Function Calling:Developer-defined code.| Hosted Tools:OpenAI-built tools. (e.g. file search, code interpreter)
一般来说可以分为两种,一种是的服务器端已经具备相关方法/工具。另一种情况是,我们自己本地准备方法工具。从OEPN-AI的流程图上,tools(第三步)也是在客户端侧。因为服务器测的方法其实也是一样的原理的所以我们重点说一下:
当我自己有一个tool,我要如何让大模型调用它,以便于他可以访问外界的知识
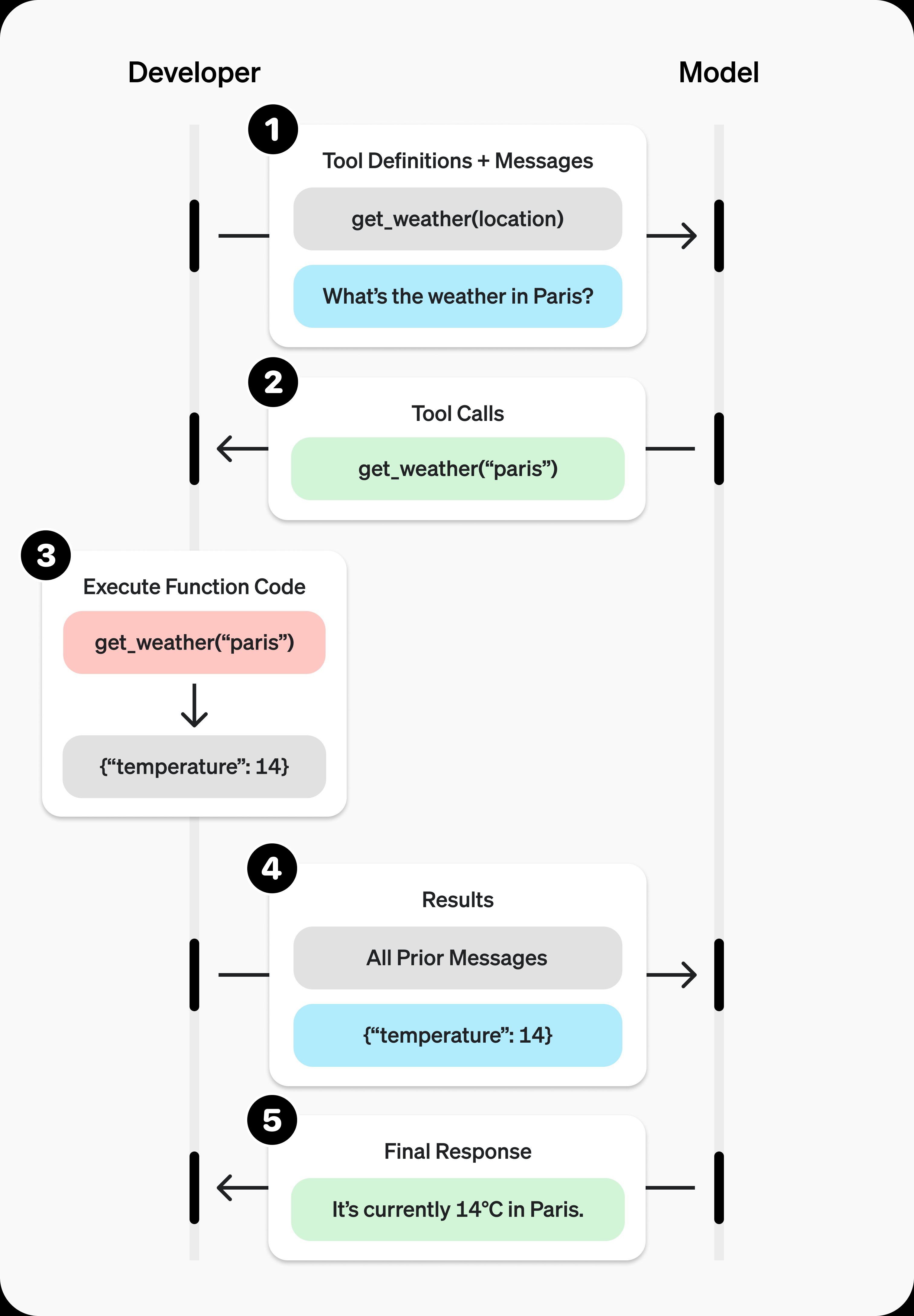
3.3 调用的流程说明
整个流程还是比较简单的:
1. 客户端发起带着tools参数的请求
2. 服务器返回一个函数名称和参数
3. 客户端用函数名称参数调用本地已经准备好的方法
4. 把方法结果加入到messages(整个对话历史),再发送给服务器
5. 服务器把结果一并输出openai、deepseek、qwen的例子都是都是查询天气,其实我觉得不够让人发散。所以从deepseek那个联网搜索的功能角度,来最小化实现一次。
4 实现细节
根据流程,我打算分块实现以下几个部分:
HINT
注意,这里只是演示怎么实现,并不代表最佳的编程方式,实际工程上的,用注册工具的思路会更加清晰
web_search_tool: 这是我们的联网搜索方法,用DrissionPage直接自动化实现搜索。tool use schema: tool use的参数schema定义,用于api传参,toolsend_message: 简单封装了一下用requests请求api,实际上对于支持OPEN AI格式的大模型,可以用openai的库,看个人偏好。handle_tool_call: 对于任何的本地的tool(如果我定义了多个)被调用后,可以在该方法内做对应的结果解析。process_conversation: 对话流程的实现。对于每次的请求,我们需要手动将message(不论是用户的request还是服务器返回的response)都添加到messages(或者叫history)里。
4.1 关键结构
4.1.1 message的结构
message就是我们构造给api发送的request或者大模型回复的response。
message可以分成几种类型:
- system(open-ai的o1会用developer来代替)、user
- assisstant
- tools
4.1.1.1 system或者user message
最常规的messsage类型,一般我们给api传的时候,system贯穿整个对话,一般只在对话开头出现一次,设定了对话的初始条件和行为模式,user则是每次用户的具体输入。两者在结构上并无区别。
{
"role": "system",
"content": "you are a helpful assistant",
"name": "a default messager" // optional
}4.1.1.2 assistant
assistant是大模型给我们的回复。除了role和content,多了几个东西。
reasoning_content:现在的reasoning模型的思考内容。如果不是reasoning模型,那就没有,目前我们先不关注。tool_calls:如果没有工具调用那该选项也是空的,但是如果有,这一json对象的则描述了我具体调用的方法和参数。(很重要,我们后续就是要用它)
tool部分的结构
# tool use schema
class FunctionCallingSchema(BaseModel):
name: str
arguments: str
# 工具调用模型
class ToolCall(BaseModel):
id: str
type: str = "function"
function: Dict[str, Union[str, Dict]]
# example
{
"id": "call_weather_123",
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_weather",
"arguments": "{\"location\": \"Shanghai, China\", \"units\": \"celsius\", \"date\": \"2024-02-02\"}"
}一个包含多次tool_calls的例子
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": "根据查询结果,明天上海将是晴天,气温23-28度。我已经帮您在日程表中添加了下午2点的户外会议。",
"reasoning_content": "1. 首先查询上海明天的天气情况\n2. 确认天气适合户外活动\n3. 在日程表中添加会议安排",
"tool_calls": [
{
"id": "call_weather_123",
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_weather",
"arguments": "{\"location\": \"Shanghai, China\", \"units\": \"celsius\", \"date\": \"2024-02-02\"}"
}
},
{
"id": "call_calendar_456",
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "add_calendar_event",
"arguments": "{\"title\": \"户外项目会议\", \"start_time\": \"2024-02-02T14:00:00\", \"end_time\": \"2024-02-02T15:30:00\", \"location\": \"公司花园\", \"description\": \"项目进度讨论\"}"
}
}
]
}4.1.2 non-stream的response结构
当我们用api,给deepseek等LLM发一个请求,那么他返回结构,主流来说,大概是这样的,包括了请求类型、请求模型、token消耗等。这里最重要的是choices字段,有我们们对话的实际内容,以及到底要不要调用tool:
{
"id": "3aed3ead-98fc-4da5-9acb-d81c1428c957",
"object": "chat.completion",
"created": 1738408513,
"model": "deepseek-chat",
"choices": [
{
"index": 0,
"message": {
"role": "assistant",
"content": "Hello! How can I assist you today? 😊"
},
"logprobs": null,
"finish_reason": "stop"
}
],
"usage": {
"prompt_tokens": 9,
"completion_tokens": 11,
"total_tokens": 20,
"prompt_tokens_details": {
"cached_tokens": 0
},
"prompt_cache_hit_tokens": 0,
"prompt_cache_miss_tokens": 9
},
"system_fingerprint": "fp_3a5770e1b4"
}4.2 关键代码
4.2.1.1 web_search_tool
第一步,必然有一个自己定义的function。这里使用了DrissionPage更直观一点(如果你用requests也行)。因为我是在云服务器上,也没装GUI,所以这里用了无头模式。如果你是windows,可以不开无头直接试试。
def web_search_tool(query: str, search_engine: str = "bing") -> Dict:
"""
使用DrissionPage进行网络搜索
:param query: 搜索关键词
:param search_engine: 搜索引擎,默认使用bing
:return: 搜索结果
"""
browser_process = None
try:
logger.info("正在启动 Chrome 浏览器...")
browser_process = subprocess.Popen(
[
"google-chrome",
"--headless=new",
"--remote-debugging-port=9222",
"--no-sandbox",
"--disable-gpu",
"--disable-dev-shm-usage",
]
)
time.sleep(2)
# 创建 ChromiumOptions 实例
co = ChromiumOptions()
co.set_argument("--headless=new")
co.set_argument("--no-sandbox")
co.set_argument("--disable-gpu")
co.set_argument("--disable-dev-shm-usage")
# 设置连接到已启动的浏览器
co.set_local_port(9222)
logger.info("正在连接到浏览器...")
page = ChromiumPage(co)
if search_engine.lower() == "bing":
# 访问Bing并搜索
logger.info(f"\n正在访问Bing搜索: {query}")
page.get(f"https://www.bing.com/search?q={query}")
time.sleep(2) # 等待搜索结果加载
# 使用xpath查找搜索结果
logger.info("正在获取搜索结果...")
search_items = page.eles('xpath://li[@class="b_algo"]')
results = []
for idx, item in enumerate(search_items):
if idx >= 10: # 只取前10个结果
break
try:
# 获取标题、链接和描述
title = item.ele("tag:h2").text.strip()
link = item.ele("tag:a").link
result = {
"title": title,
"link": link,
}
# 流式输出每个搜索结果
logger.info(f"\n获取到第 {idx + 1} 个结果:")
logger.info(f"标题: {title}")
logger.info(f"链接: {link}")
results.append(result)
except Exception as e:
logger.info(f"解析第 {idx + 1} 个结果时出错: {str(e)}")
continue
if not results:
return {
"tool_call_status": "error",
"error_message": "未找到有效的搜索结果",
}
return {
"tool_call_status": "success",
"search_results": results,
"metadata": {
"engine": "bing",
"query": query,
"total_results": len(results),
# 添加时间戳和结果校验
"timestamp": int(time.time()),
"result_hash": hash(str(results)),
},
}
except Exception as e:
error_msg = str(e)
logger.info(f"搜索过程中出错: {error_msg}")
return {"tool_call_status": "error", "error_message": error_msg}
finally:
# 清理资源
try:
if "page" in locals():
page.quit()
except:
pass
try:
if browser_process:
logger.info("正在关闭浏览器进程...")
browser_process.terminate()
browser_process.wait(timeout=5)
except:
pass4.2.1.2 tool use schema
有了方法,我们还要根据大模型调用的规范,在向api请求的时候,带上我们的tools列表。这可以是多个也可以是一个。
这里有三个地方要注意:
- tools是一个list,在这里我写了两个tool,尽管这次我只会调用一个。原因是LLM会根据prompt和工具调用的参数来决定具体调用什么tool。所以你可以把你所有的tool都传给它。
- 我设置了一个is_user_message,目的是判断目前send的message角色是不是user,不是user则不给tool置为none,避免system message触发了调用。
- description:必须描述正确,这里的description不是docstring,而是描述function的具体使用场景的。既要注意不要和其他tool有冲突,也要注意描述的场景覆盖到位。
tools = [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "web_search",
"description": """用于获取实时信息或专业知识。适用场景:
4. 需要最新的新闻、数据或市场信息
5. 需要特定领域的专业技术细节
6. 需要验证某个说法或数据的准确性
7. 需要了解产品、技术或行业的最新发展
搜索结果将包含标题和链接,可用于进一步分析和参考。""",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"query": {
"type": "string",
"description": "搜索关键词,应该精确描述所需信息",
},
"search_engine": {
"type": "string",
"description": "搜索引擎选择",
"enum": ["bing"],
},
},
"required": ["query"],
},
},
},
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "prepare_project_structure",
"description": """用于分析项目的目录结构。适用场景:
8. 需要了解项目整体架构
9. 进行代码审查或技术评估
10. 提供项目改进建议
11. 解决项目相关的技术问题
返回项目的文件和目录层次结构,包含文件名和类型信息。""",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"root_dir": {
"type": "string",
"description": "项目根目录路径,使用相对或绝对路径",
},
"exclude_dirs": {
"type": "array",
"items": {"type": "string"},
"description": "需要排除的目录列表,如node_modules、.git等",
},
},
"required": ["root_dir"],
},
},
},
]4.2.1.3 send message
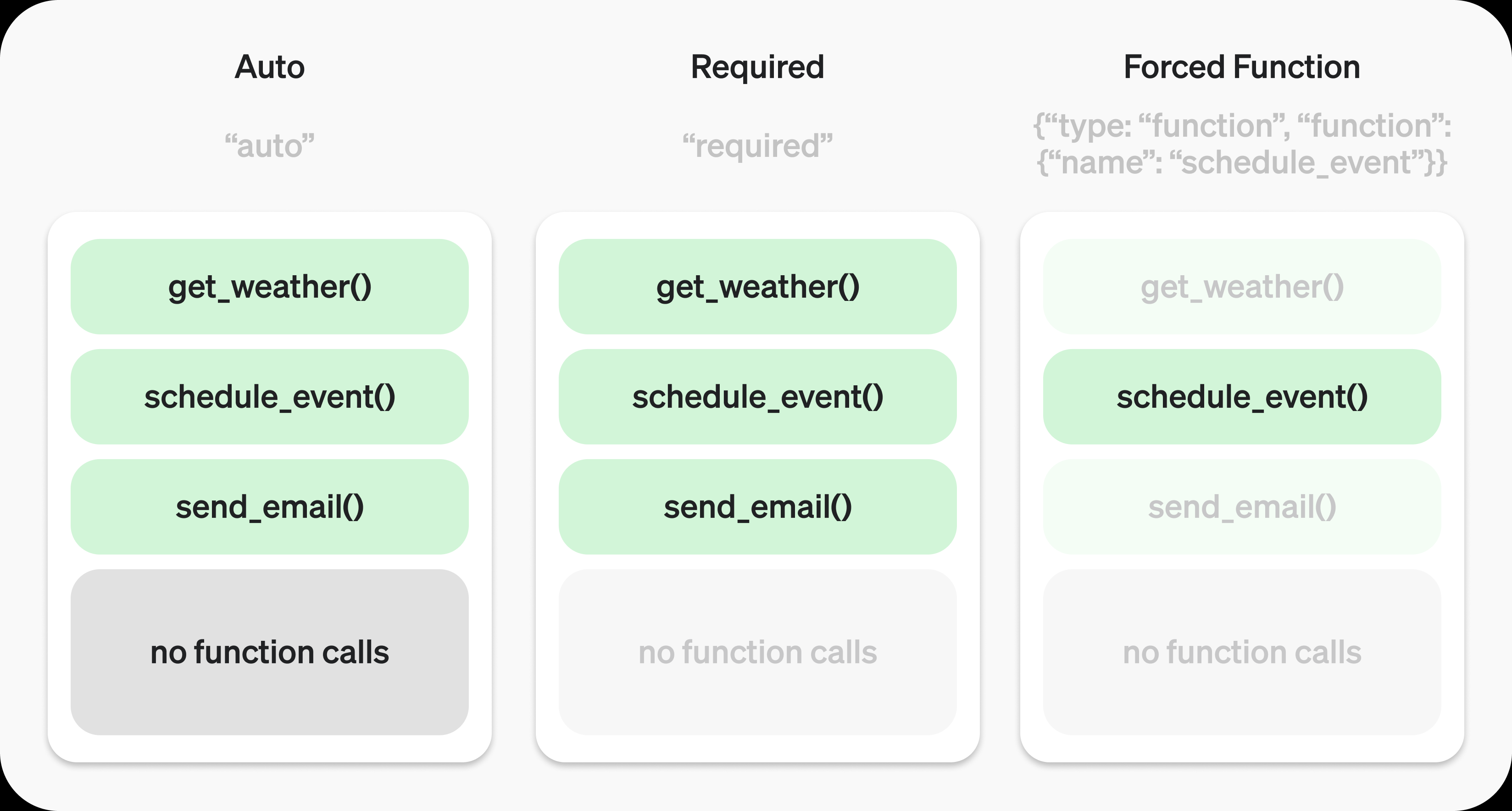
send_message主要是封装了请求。这里要注意的是data里的tool_choice,一般来说使用"auto"就能让大模型自己决定什么时候用什么tool。
Auto模式:模型可以自由决定是否调用工具以及调用几个。
Required模式:模型必须至少调用一个工具。
Forced Function模式:模型必须且只能调用指定的那个工具。
def send_messages(messages):
"""使用requests发送消息到API"""
try:
global tools
api_key = os.getenv("DEEPSEEK_API_KEY")
headers = {
"Authorization": f"Bearer {api_key}",
"Content-Type": "application/json",
}
# 检查最后一条消息是否为用户消息
is_user_message = messages and messages[-1]["role"] == "user"
data = {
"model": "deepseek-chat",
"messages": messages,
"tools": tools if is_user_message else [],
"tool_choice": "auto" if is_user_message else "none",
"temperature": 0.7,
"max_tokens": 4096,
}
response = requests.post(
"https://api.deepseek.com/v1/chat/completions", headers=headers, json=data
)
logger.debug(f"API调用结果: {response.json()}")
if response.status_code != 200:
return {
"content": f"API调用失败: HTTP {response.status_code}, {response.text}"
}
result = response.json()
return result["choices"][0]["message"]
except Exception as e:
return {"content": f"发生错误: {str(e)}"}4.2.1.4 handle_tool_calls
不同的tool有不同的返回值结构。可以在这里的进行处理。
def handle_tool_calls(message: Message) -> Optional[List[ToolResponse]]:
"""处理工具调用的函数"""
if not message.tool_calls:
return None
results: List[ToolResponse] = []
for tool_call in message.tool_calls:
args = json.loads(tool_call.function["arguments"])
tool_response = ToolResponse(tool_call_id=tool_call.id, content="")
try:
if tool_call.function["name"] == "web_search":
result = web_search_tool(
query=args["query"], search_engine=args.get("search_engine", "bing")
)
# 验证结果格式
web_search_response = WebSearchResponse(**result)
# 使用 json.dumps 处理中文编码
tool_response.content = json.dumps(
web_search_response.model_dump(), ensure_ascii=False
)
results.append(tool_response)
elif tool_call.function["name"] == "prepare_project_structure":
result = prepare_project_structure_tool(
root_dir=args.get("root_dir", "."),
exclude_dirs=args.get("exclude_dirs", None),
)
tool_response.content = json.dumps(result, ensure_ascii=False)
results.append(tool_response)
except Exception as e:
logger.info(f"执行工具 {tool_call.function['name']} 时出错: {str(e)}")
error_response = ToolCallStatus(
tool_call_status="error", error_message=str(e)
)
# 使用 json.dumps 处理中文编码
tool_response.content = json.dumps(
error_response.model_dump(), ensure_ascii=False
)
results.append(tool_response)
return results4.2.1.5 system prompt
system prompt不仅决定是否使用工具,还会影响工具使用的方式、时机和范围。通过合理配置system prompt,我们可以更精确地控制和优化模型的工具调用行为。
default_system_message = {
"role": "system",
"content": """你是一个智能助手,擅长解决各类问题和完成各种任务。你具备以下能力:
12. 信息获取与分析
- 当需要最新信息、专业知识或验证信息时,可以使用web_search工具
- 对搜索结果进行分析整合,提取关键信息
- 结合已有知识和搜索结果给出全面的回答
13. 项目分析与理解
- 需要了解项目结构时,可使用prepare_project_structure工具
- 基于目录结构分析项目特点和技术栈
- 提供相关建议和改进方案
工具使用原则:
14. 根据问题需求判断是否需要使用工具
15. 优先使用自身知识回答,在必要时补充工具信息
16. 可以组合多个工具以获得完整信息
17. 确保回答准确性和时效性
回答要求:
18. 答案应清晰、准确、有逻辑性
19. 适当引用信息来源
20. 必要时分点说明或使用Markdown格式增加可读性
21. 对不确定的信息要说明局限性""",
}4.2.1.6 process_conversation
流程请求的最后封装,这里要注意的就是,当本地执行完tool调用以后,要将结果封装成tool message再发给服务器。
这里有两个选择:
- 我们可以显式的构造一个请求,提供一个新的prompt,强制改变大模型后续的执行逻辑
- 我们也可以直接把tool的调用结果以tool message(参照message结构部分)去构造,让大模型完成剩下的逻辑。
def process_conversation(messages: Optional[List[Dict[str, Any]]] = None):
"""
处理对话流程
Args:
messages: 可选的初始对话列表。如果不提供,将使用默认的system prompt和用户消息
"""
conversation_messages = [default_system_message]
# 如果提供了自定义消息,添加到system prompt之后
if messages:
conversation_messages.extend(messages)
try:
logger.info("\n开始请求对话...")
response = send_messages(conversation_messages)
if isinstance(response, dict):
# 确保response包含必需的role字段
if "role" not in response:
if "error" in response:
logger.error(f"API返回错误: {response.get('error')}")
return
# 如果是错误消息,设置为assistant角色
response["role"] = "assistant"
message = Message(**response)
else:
logger.error("Invalid response format")
return
if message.tool_calls:
# 添加助手消息到历史
assistant_message = Message(
role="assistant", content=None, tool_calls=message.tool_calls
)
conversation_messages.append(assistant_message.model_dump())
# 处理所有工具调用
tool_results = handle_tool_calls(message)
if tool_results:
# 添加工具响应到消息历史
for result in tool_results:
tool_message = Message(
role="tool",
content=result.content,
tool_call_id=result.tool_call_id,
)
conversation_messages.append(tool_message.model_dump())
summary_response = send_messages(conversation_messages)
if isinstance(summary_response, dict):
try:
summary_message = Message(**summary_response)
if summary_message.content:
logger.info(
f"\n最终总结:\n{summary_message.content}"
)
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"处理总结时出错: {str(e)}")
else:
logger.error("Invalid summary response format")
else:
logger.info(f"\nAssistant回复:{message.content}")
logger.info("\n-----------对话轮次结束---------------")
except Exception as e:
logger.info(f"处理对话时发生错误: {str(e)}")
import traceback
traceback.print_exc()5 总结
5.1 遇到的问题
在调用tools时,实际遇到了一些问题,例如无线调用、连续调用以及不触发的情况。目前,tool use的功能还不够完善。以下是需要注意的几个关键点:
- System Message的判断:需要对
system message进行适当的判断和处理。 - 影响调用的因素:包括
system prompt、tools的schema中的description、user prompt等,这些内容必须清晰明确。此外,请求tool_choice时的模式也需要注意。 - 利用大模型的能力:非标要的情况下,尽量依赖大模型自身的能力,而不是通过
user prompt强行改变其行为。
5.2 心得体会
system prompt和tool use schema一定要写好,几乎90%的问题都是没有描述清楚tool use里的description。总得来说:
- 功能边界:所以我们要用明确的功能和领域去隔离不同的使用场景,包括可用和不可用的场景
- 此工具用于互联网实时信息搜索。
- 此工具用于pdf文件的读写操作,其他类型文件不可使用该工具。
- 参数规范:在参数的description中应当说明参数类型和格式要求:
- location仅用于具体的地理位置。
- query长度输入不超过100个字符。
- 意图识别:对于复杂的自然语言场景,可以根据场景包含意图识别的说明:
- 当用户询问的中包含
最新信息、实时数据字眼时使用 - 用户询问模式如“最近有什么....”、“如何评价..........."句式时
- 用户询问内容包含
**等内容,禁止使用的该工具进行联网搜索。
- 当用户询问的中包含
- 优先级:复杂场景时,应当说明错误处理、优先级和关联性
- 优先使用本地数据库查询,数据不足时使用联网搜索。仍然不足时回复“数据不足以回答”
实际上,总结出这些看着很简短,但是不同场景的真实感受,还得自己不断修改system prompt、user prompt、description等多次尝试,才会找到属于自己项目的最佳实践
最后再抛出一个例子
5.3 一个例子:一句话让大模型为我调用多次方法。
比如我的prompt是:
{
"role": "user",
"content": "宝马X1多少钱,小米Su7多少钱,这两个车哪个更能彰显身份地位?"
}那么我会得到一个这样的response。 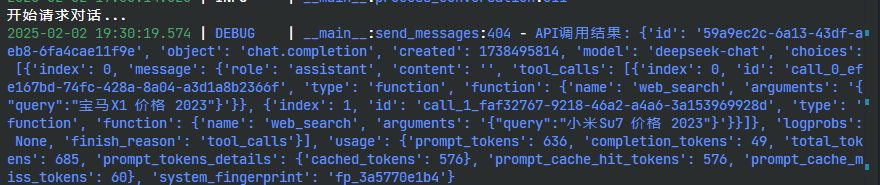 image.png
image.png
你会注意到tools_calls这个字段有两个tools调用的结果。所以,不是一个问题它就只执行一次。
"tool_calls": [
{
"index": 0,
"id": "call_0_efe167bd-74fc-428a-8a04-a3d1a8b2366f",
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "web_search",
"arguments": "{\"query\":\"宝马X1 价格 2023\"}"
}
},
{
"index": 1,
"id": "call_1_faf32767-9218-46a2-a4a6-3a153969928d",
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "web_search",
"arguments": "{\"query\":\"小米Su7 价格 2023\"}"
}
}
]5.4 完整代码
我把完整代码放在: https://github.com/re0phimes/BlogCode
6 参考
[1] Anthropic. Tool use (function calling) - Anthropic Documentation [EB/OL]. (2024-10)[2025-02-02]. https://docs.anthropic.com/en/docs/build-with-claude/tool-use.
[2] DeepSeek. Function Calling | DeepSeek API Documentation [EB/OL]. (2024)[2025-02-02]. https://api-docs.deepseek.com/zh-cn/guides/function_calling/.
[3] Qwen Team. Function Calling - Qwen Documentation [EB/OL]. (2024)[2025-02-02]. https://qwen.readthedocs.io/en/latest/framework/function_call.html.
[4] OpenAI. Function calling - OpenAI API Documentation [EB/OL]. (2024)[2025-02-02]. https://platform.openai.com/docs/guides/function-calling.
[5] OpenAI. API Reference - OpenAI API Documentation [EB/OL]. (2024)[2025-02-02]. https://platform.openai.com/docs/api-reference/chat/object.